To tell if CPU voltage is too low, monitor system stability and check for frequent crashes or failure to boot. Performance issues such as slow operation or hardware malfunction could also indicate insufficient voltage.
Determining the right voltage for a CPU is essential for optimal computer performance and longevity. CPUs require a specific voltage range to operate effectively, and deviations from this can lead to various issues. A too-low voltage often results in system instability, which can manifest as random restarts or an inability to run intensive applications.
This is because the processor isn’t receiving enough power to maintain regular operations under load. Regular system monitoring tools can help flag potential voltage-related problems, and BIOS or UEFI settings often display the current CPU voltage for review. Ensuring your CPU operates within the recommended voltage range will help maintain a stable and reliable system.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Introduction To Cpu Voltage
Understanding the importance of CPU voltage is crucial for any computer enthusiast or professional. The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the brain of your computer. It needs the right amount of electrical power to operate efficiently. This power is known as the CPU voltage. Getting the voltage right is like hitting the sweet spot for your CPU’s performance and longevity.
The Role Of Voltage In Cpu Performance
Consider voltage as the lifeblood for your CPU’s performance. It’s the critical factor that fuels the processor to run applications, perform tasks, and process data. Just as your body needs the right amount of energy to function, your CPU needs the right voltage to perform at its best.
- Stable voltage ensures smooth CPU operations.
- Inconsistent or low voltage can lead to performance issues.
Consequences Of Inadequate Power Supply
Inadequate CPU voltage can have a ripple effect on your computer’s performance. A power supply that fails to deliver the necessary voltage can lead to numerous problems, potentially damaging the CPU or other components.
| Consequence | Impact on CPU |
|---|---|
| System Instability | Unexpected crashes or restarts |
| Reduced Performance | Slower processing speeds |
| Hardware Damage | Potential permanent CPU failure |
Identifying and addressing CPU voltage issues early helps maintain optimal system health.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Recognizing Symptoms Of Low Cpu Voltage
Is your computer acting up? It might be due to low CPU voltage.
Like a car needs the right fuel mix, your CPU needs the correct voltage to run smoothly. Here are the signs that show your CPU might be getting too little power:
System Instability And Frequent Crashes
An unstable system is a red flag. Your computer may:
- Shut down unexpectedly.
- Show the dreaded blue screen of death (BSOD).
- Reboot on its own.
Difficulty Booting And Power Fluctuations
Struggling to start up your PC could point to power issues. Watch out for signs like:
- Computer turns off and on repeatedly.
- Long waits before the operating system loads.
Power fluctuations also lead to erratic behavior.
Decreased Performance And Throttling
If your PC slows down, it might be due to throttling. This means:
- Games and apps run slower than usual.
- Multitasking becomes a nightmare.
Physical Signs: Buzzing Or Beeping Sounds
Be alert to unusual sounds coming from your computer:
| Buzzing | Beeping |
|---|---|
| May indicate electrical issues. | Often a sign of power problems. |
These sounds often mean the CPU isn’t getting enough juice.
Diagnosing The Voltage Issue
Diagnosing the CPU Voltage Issue becomes crucial when systems exhibit instability, unexpected shutdowns, or fail to boot. Correctly setting the CPU voltage is key for optimal performance and hardware longevity. We will explore the signs of voltage-related problems and how to verify if your CPU voltage is indeed too low.
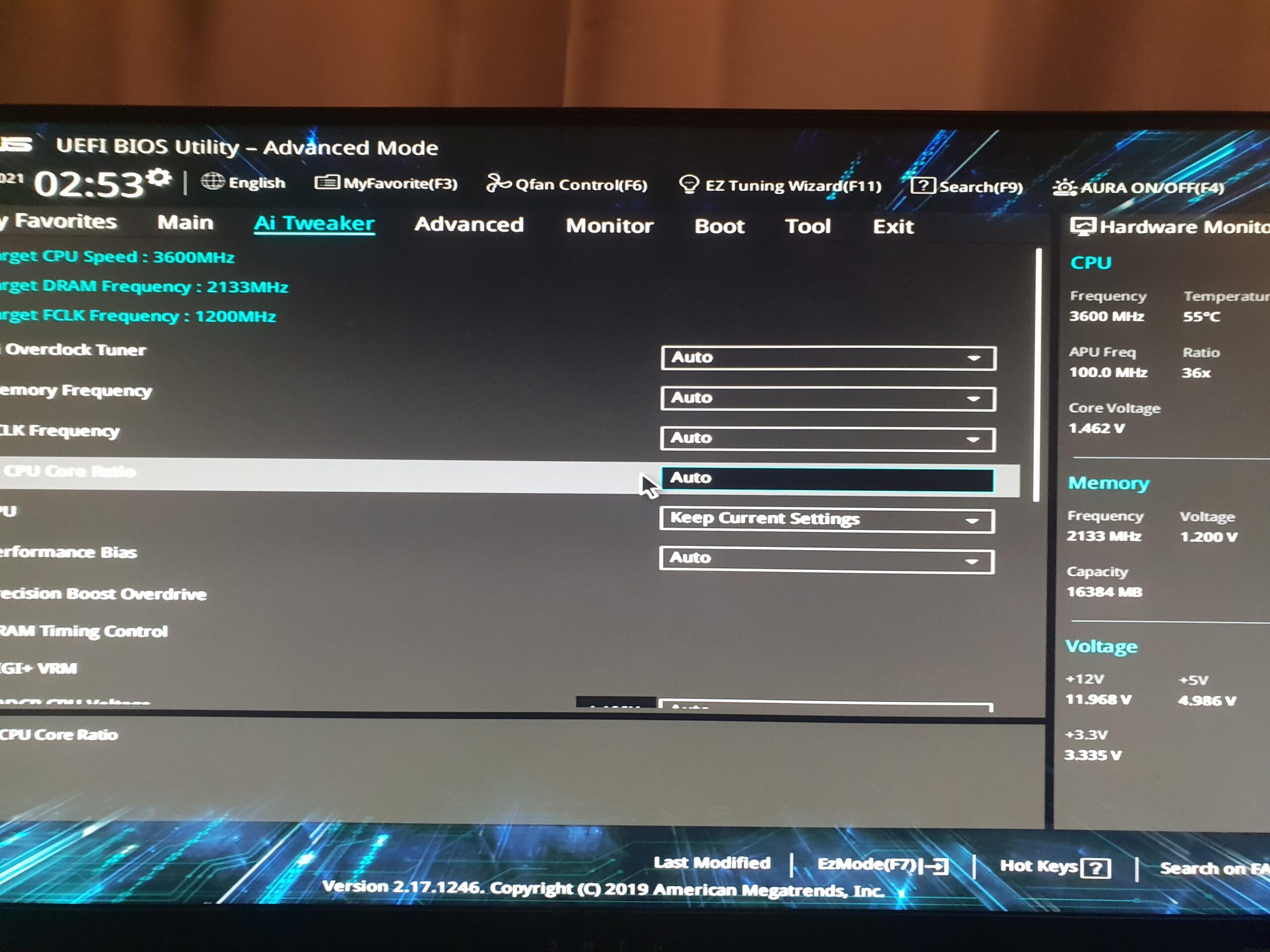
Using Bios To Check Voltage Settings
The BIOS or UEFI is a pivotal starting point for diagnosing CPU voltage issues. Here’s how to utilize it:
- Restart your computer.
- Press the designated key to enter the BIOS/UEFI. This key is usually Del, F2, or Esc.
- Look for sections labeled ‘Overclocking’, ‘Power Management’, or ‘Hardware Monitor’.
- Find the CPU Voltage readings and compare them with your CPU’s recommended settings.
Software Tools For Monitoring Cpu Voltage
Diverse software tools can aid in tracking CPU voltage in real-time. Examples include:
- CPU-Z: Displays in-depth info about the CPU, including the voltage.
- HWMonitor: Monitors various hardware parameters, voltage included.
- Core Temp: Focuses on the CPU’s temperature and voltage metrics.
These tools can provide a quick glimpse of whether the CPU voltage deviates from the norm.
Consulting The Motherboard’s User Manual
Motherboard manuals are a reliable reference for proper CPU voltage settings. Steps to consider:
- Locate the manual that came with your motherboard.
- Search for the specifications section outlining default voltage settings.
- Match the BIOS CPU Voltage readings with those in the manual to ensure consistency.
Following this guide assists in diagnosing if the CPU voltage set is too low for your system’s demands.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Adjusting Cpu Voltage
Ensuring your CPU has the correct voltage is crucial for its performance and longevity. A voltage that’s too low can lead to system instability or failure to boot. Conversely, too high a voltage can cause overheating and damage your CPU. This guide offers a clear roadmap to adjust your CPU voltage safely.
Steps To Safely Increase Voltage In Bios
Changing the CPU voltage, often called “overvolting”, must be done with care. Always ensure your CPU is running within safe temperature limits.
- Restart your computer and tap the key that enters BIOS Setup. This key is usually F2, Del, or Esc.
- Navigate to the Advanced Tab or CPU settings section.
- Look for CPU VCore or Core Voltage options.
- Incrementally increase the voltage by the smallest possible amount.
- Save the changes and exit BIOS.
- Monitor CPU temperatures using a hardware monitoring tool.
After each increment, check for system stability through stress testing. If instability occurs, revert to the last stable voltage.
Understanding Voltage And Clock Speed Relations
The relationship between voltage and clock speed is double-edged. Higher voltages can support higher clock speeds, leading to better performance. Yet, increased voltage leads to more heat generation.
Finding the balance between voltage and clock speed is essential. Using benchmarking tools, one can fine-tune their settings. This ensures the best possible balance of performance and heat.
Remember, it’s vital to increase voltage only to levels that your CPU cooler can handle. Keep an eye on critical limits suggested by the CPU manufacturer.
Preventing Low Voltage Complications
Ensuring your CPU runs with the right voltage is critical for system stability and longevity. CPUs require a precise voltage to operate correctly. Too low a voltage can lead to system instability, crashes, or even hardware damage over time.
Choosing The Right Power Supply
The power supply unit (PSU) is the heart of your computer’s electrical system. A high-quality PSU can provide steady voltage and prevent issues associated with low voltage. Consider these factors when selecting a PSU:
- Wattage rating should exceed your system’s requirements.
- Look for 80 PLUS certification for energy efficiency.
- Choose reputable brands with good warranties.
- Check for comprehensive protection features (over-voltage, under-voltage, short circuit protection).
Regular Maintenance And Firmware Updates
Regular system maintenance, including firmware and BIOS updates, can optimize voltage regulation. These updates might fix underlying bugs that affect your CPU’s voltage.
- Check your motherboard manufacturer’s website for updates.
- Apply updates following manufacturer instructions.
- Monitor system stability post-update.
Balancing Overclocking With Voltage Stability
Overclocking boosts CPU performance but requires more voltage. Maintain voltage stability with these steps:
- Gradually increase the CPU’s clock speed.
- Use stress testing software to check stability at each step.
- Adjust voltage in small increments, only as needed.
- Ensure cooling systems can handle increased heat from overclocking.
When To Seek Professional Help
Determining if your CPU voltage is too low can be tricky. Signs of inadequate voltage may include system instability, unexpected shutdowns, or failure to boot. While some enthusiasts feel comfortable adjusting settings in the BIOS, it’s crucial to know when to call in the experts. Let’s dive into scenarios that signal a need for professional intervention.
Identifying Hardware Failures
- Random crashes or blue screens suggest serious issues.
- When the PC fails to boot multiple times, hardware could be at fault.
- If overclocking attempts lead to instability, professional guidance may prevent damage.
Should these symptoms persist despite basic troubleshooting, it’s time to consult a technician. They can run comprehensive tests to rule out hardware failure and ensure the CPU receives correct voltage.
Warranty And Technical Support Options
Don’t overlook warranty terms. Manufacturers often offer dedicated support for technical issues.
| Manufacturer | Warranty Period | Support Contact |
|---|---|---|
| Brand A | 3 Years | Support Line: 123-456-7890 |
| Brand B | 5 Years | Support Line: 098-765-4321 |
Check your warranty status online or in your paperwork. If under warranty, contact support before opening your system. This action could void your warranty. Professional technicians provided by the manufacturer can diagnose and fix the problem.
Frequently Asked Questions Of How To Tell If Cpu Voltage Is Too Low
What Are Symptoms Of Low Cpu Voltage?
A CPU with low voltage can exhibit slow performance, system instability, and unexpected shutdowns. It can also lead to difficulty in booting up and may cause random system crashes.
How Can I Check My Cpu’s Voltage?
To check your CPU’s voltage, use the BIOS/UEFI settings or reliable software monitoring tools like CPU-Z or HWMonitor. These programs display real-time voltage readings for your CPU.
Why Is Correct Cpu Voltage Important?
Proper CPU voltage ensures optimal performance, stability, and longevity of your processor. Incorrect voltage can cause hardware malfunction, data corruption, and reduced lifespan of the CPU.
Can Low Voltage Damage A Cpu?
While low voltage itself typically doesn’t cause damage, it can lead to system instability, poor performance, or an inability to boot. Continuous operation under these conditions may indirectly harm the CPU.
Conclusion
Assessing CPU voltage is essential for stable computer performance. Symptoms like frequent crashes or sluggish behavior can signal an issue. Utilize your BIOS settings or dedicated software to monitor and adjust levels if necessary. Remember, optimal voltage safeguards both your CPU’s functionality and your peace of mind.
Keep it balanced, and your system should run smoothly.