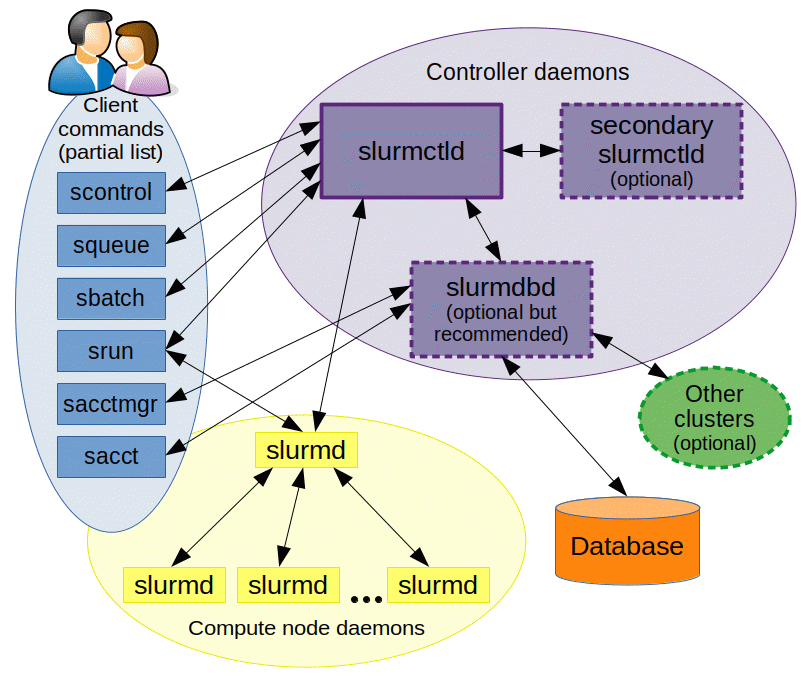
A CPU, or Central Processing Unit, resembles a small rectangular chip with many tiny, intricate connections. It’s often secured onto a motherboard inside a computer.
Exploring the core of computing, the CPU can be thought of as the brain of a computer, handling instructions and processing data from computer programs. This silicon chip is usually housed inside a ceramic or metal package and is mounted securely onto the motherboard, which connects it to other components.
The top of the CPU often bears the manufacturer’s logo and information about the model. For effective heat dissipation—a critical aspect of CPU operation—most CPUs are topped with a metal heat spreader, which a heat sink or cooling fan generally accompanies. Enhancing visibility in search results, it’s important to note that manufacturers, such as Intel and AMD, design CPUs with varying core counts, clock speeds, and processing capabilities, each tailored for specific types of computers from laptops to servers. Understanding what a CPU looks like demystifies one of the most vital parts of modern technology.

Credit: www.microsoft.com
Anatomy Of A Cpu
Unlock the mystery of the modern computer’s brain: the CPU. Learn what lies beneath the sleek exterior of this powerhouse. It’s not just a chip; it’s a marvel of engineering.
Silicon Heart: Cpu Die
The core of a CPU is the die. Made from pure silicon, this tiny slab houses billions of transistors. These transistors work together to process data.
- Transistors: Switches controlling the flow of electricity.
- Circuits: Connect transistors and define the CPU’s capabilities.
- Layout: Designed for efficiency and speed.
Manufacturers engrave patterns on the die to form circuits. This die is the true essence of a CPU.
The Protective Shell: Heat Spreader
Above the die lies the heat spreader. This is a metal cap that protects the silicon die. It also spreads out the heat the CPU generates.
| Material | Function |
|---|---|
| Metal | Shields the die |
| Thermal Paste | Improves heat transfer |
Thermal paste sits between the die and spreader. It helps to transfer heat. The heat spreader ensures the CPU operates at safe temperatures.
Complexity Beneath The Pins
At first glance, a CPU looks like a simple piece of hardware with metallic contacts. Each tiny square inch hides a world teeming with complexity. Let’s delve into the intricate designs that live beneath the seemingly straightforward exterior of a Central Processing Unit.
Pin Layout: The Cpu’s Fingertips
The rows of pins you see on a CPU are more than tiny pieces of metal. They create a vital link between the processor and the motherboard. This connection allows the CPU to communicate with other components. Think of them as the CPU’s fingertips, touching the lifeblood of the computer’s circuitry.
- Different CPUs have unique pin configurations, known as the socket type.
- Pin layout aligns perfectly with the motherboard to ensure proper functionality.
- These pins supply power and facilitate communication channels.
Microscopic Marvels: Transistors And Circuits
Beneath the CPU casing lies a silicon maze of transistors and circuits. It’s a miniature city where millions of operations occur every second. This is the real magic of modern computing. Each transistor acts as a switch, controlling the flow of electrical signals.
- Transistors scale down to incredibly small sizes, thanks to modern nanotechnology.
- Their on-and-off states represent the binary code that runs our software.
- Integrated circuits connect these transistors, creating a network of pathways for data.
With advancements in microprocessor technology, CPUs continue to evolve. This progress means more power and efficiency packed into the same small chip, ready to take on complex tasks.
From Silicon To Performance
The journey of a CPU from a piece of silicon to a powerhouse of computing involves intricate design and advanced engineering. At its heart, this transformation hinges on two major characteristics that define a CPU’s capabilities: core count and clock speeds. Let’s explore how these factors multiply processing power and set the rhythm of processing.
Core Count: Multiplying Processing PowerCore Count: Multiplying Processing Power
CPU cores are like workers in a factory – the more you have, the more tasks you can handle simultaneously. Not long ago, single-core processors were the norm, but today, multitasking demands have led to CPUs boasting multiple cores.
| Core Count | Type of CPU | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 2-4 | Dual/Quad-core | Basic tasks |
| 6-8 | Hexa/Octa-core | Advanced gaming |
| 12+ | Multicore | Workstations |
- Dual-core CPUs handle basic computing tasks.
- Quad-core and beyond enable advanced gaming and professional applications.
Clock Speeds: The Rhythm Of Processing
Imagine a metronome – that’s what clock speed is for a CPU. It ticks at a steady pace, dictating how many operations the CPU can perform each second. Measured in gigahertz (GHz), higher clock speeds generally mean a faster processor.
- Base clock speed runs at a guaranteed minimum frequency.
- Boost clock speed kicks in for demanding tasks.
Here’s a quick look at clock speeds in action:
- 3.0 GHz may be fine for everyday tasks.
- 5.0 GHz and above targets enthusiast gamers and professionals.

Credit: news.mit.edu
Heat Management Components
Understanding the CPU’s battle with heat is crucial when considering its performance and lifespan. A CPU may look like a small, flat piece of silicon, but it generates a lot of heat. The heat management components are central to keeping it cool and functioning at its best. These components protect the CPU from overheating. Without them, the CPU could overheat and potentially fail. Let’s delve into the key elements responsible for heat management in CPUs.
Integrated Heat Spreaders: Combatting Cpu Heat
The integrated heat spreader, or IHS, acts as a shield for the CPU’s delicate core. Made of metal, the IHS distributes heat away from the CPU evenly. Think of it as a metal cap that sits on top of the CPU chip. It takes the heat that the CPU makes and spreads it out. This way, it can be cooled down easily by fans or liquid coolers. The IHS is a critical first line of defense against high temperatures.
Thermal Compounds: Bridging The Gap
Even with an IHS in place, tiny imperfections can cause gaps that trap heat. This is where thermal compounds come in. They fill these gaps between the IHS and the cooler placed on top of it. The compounds are also known as thermal paste or grease. They help transfer heat more effectively. They make sure there is a good connection between the CPU and its cooler. A well-applied thermal compound can significantly lower CPU temperatures. It ensures optimal heat conduction.
- Types of Thermal Compounds:
- Metal-based
- Ceramic-based
- Silicon-based
Choosing the right thermal compound and applying it correctly is key to maintaining CPU health. A good paste can make a big difference in cooling your CPU.
Architectural Evolution
The architectural evolution of CPUs unfolds as a captivating tale of innovation and transformation. From the early days of bulky, simple processors to the intricate systems of today, the journey has been nothing short of remarkable. This section explores the changes over generations and ponders future advances.
Generational Shifts: How Cpus Have Changed
When delving into the generational shifts, it’s evident that CPUs have undergone vast changes. The original designs, reliant on basic technology, set the foundation for what was to come.
- Speed: Clock speeds have soared, allowing faster processing.
- Miniaturization: Components have shrunk, boosting efficiency and saving space.
- Core Count: The rise in core numbers enhances multitasking and performance.
Both design complexity and power management have evolved. Early CPUs were designed without energy efficiency in mind, while modern iterations prioritize minimal power for optimal function.
This evolution is clear when comparing vintage CPUs, with their limited capabilities and simple structures, to modern multi-core designs that offer superior speed and multitasking abilities.
Future Designs: Projecting Cpu Developments
Anticipation builds as we consider the future prospects of CPU designs. Researchers relentlessly pursue advances in technology to create even more powerful processors.
Upcoming developments may include:
- Quantum Computing: A revolutionary paradigm potentially offering immense speed.
- 3D Stacking: An architectural approach to layering components for higher performance.
- Energy Efficiency: Continuous improvements to make CPUs more eco-friendly.
These advancements promise to redefine what we expect from the heart of our computing devices. While only time will tell the extent of these changes, the trajectory points to an exciting horizon for CPU architecture.

Credit: www.wired.com
Frequently Asked Questions For How Does Cpu Look Like
How Do I Identify My Cpu?
To identify your CPU, check the computer’s system information. On Windows, press ‘Ctrl + Shift + Esc’ to open Task Manager, and then click on the ‘Performance’ tab. For Mac, access ‘About This Mac’ from the Apple menu.
What Does Cpu Core Look Like?
A CPU core is a small, integrated circuit with distinct sections for processing, control, and cache memory, visually resembling a complex electronic chip.
What Is An Example Of A Cpu?
An example of a CPU is the Intel Core i7-10700K, which is a popular processor for high-performance computing tasks.
What Is The Physical Description Of A Cpu?
A CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is a small, rectangular component with numerous metallic connectors or pins on one side. It is typically encased in a protective shell and mounted on the motherboard within a computer.
Conclusion
Understanding the appearance of a CPU is crucial for anyone interested in technology. It’s the brain of your computer, after all. By recognizing its characteristics and how it fits within your system, you’re better equipped to handle upgrades and troubleshoot with confidence.
Keep exploring, stay informed, and enjoy the journey through the ever-evolving landscape of computing tech.